삼각 함수 & 구면좌표계-01
삼각 함수 :
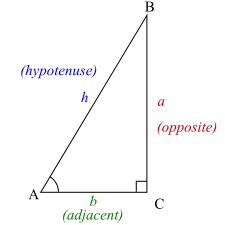

삼각함수 항등식 :
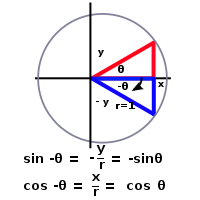
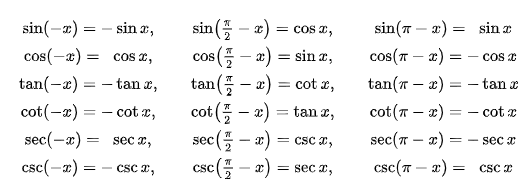
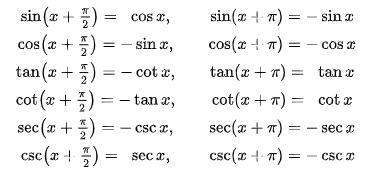
2019/09/02 - [C++(Math&알고리즘)] - Rotation Matrix
Rotation Matrix
이전링크에서는 rotation에 대한 설명이 없어서 이부분에 대해서 정리를 해볼까 합니다. 2019/08/20 - [C++(DirectX)] - C++ W(world) V(view) P(projection) matirx C++ W(world) V(view) P(projection) matirx k..
kwaksh2319.tistory.com
구면 좌표계 :
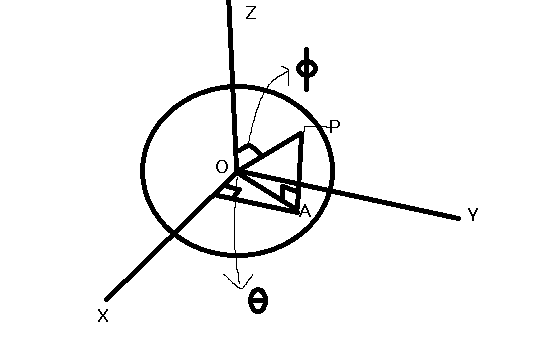
그림을 보시면서 천천히 따라 가시면 될것 같습니다 .
먼저 OA 직선을 구하려고 할떄 OP의 직선과 파이를 알고 있다면
$$OA=OP*\cos(\pi/2-\phi)$$
여기서 삼각함수 항등식에 의하면
$$OA=OP*\sin(\phi)$$
다음은 P의 좌표인 (x,y,z)를 구해보겠습니다.
$$x=OA*\cos(\theta)$$
왜냐하면 삼각형을 떼서 보면
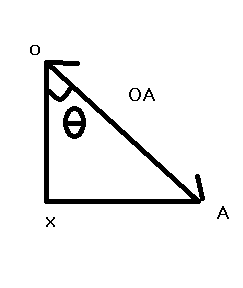
위의 그림과 같다. 그렇다면 코사인세타는
$$OX/OA=\cos(\theta)$$
이다
그래서
$$x=OA*\cos(\theta)$$
$$OX/OA=\cos(\theta)$$
$$OA*OX/OA$$
입니다.
그러면
$$OX$$
가 남습니다.
즉 x좌표는
$$x=OA*\cos(\theta)$$
입니다.
그렇다면
위에서 OA 값은
$$OA=OP*\sin(\phi)$$
였습니다.
그걸 변경을 하면
$$x=OA*\cos(\theta)$$
$$x=OP*\sin(\phi)\cos(\theta)$$
이런식으로 변경이 됩니다.
다른 좌표들도 마찬가지로
정리해보면
x좌표
$$x=OA*\cos(\theta)$$
$$x=OP*\sin(\phi)\cos(\theta)$$
y좌표는
$$y=OA*\cos(\pi/2-\theta)$$
$$y=OP*\sin(\phi)*cos(\pi/2-\theta)$$
$$y=OP*\sin(\phi)\sin(\theta)$$
z 좌표는
$$z=OP*\sin(\pi/2-\phi)$$
$$z=OP*\cos(\phi)$$
이다.
그렇다면 구의
$$x^2+y^2+z^2=OP^2$$
를 증명하자면
위에 구한 좌표값을 전부 넣어보니다.
$$x^2+y^2+z^2=OP^2$$
$$x^2+y^2+z^2=(OP*\sin(\phi)\cos(\theta))^2+$$
$$(OP*\sin(\phi)\sin(\theta))^2+(OP*\cos(\phi))^2$$
식을 풀면
$$(OP^2*\sin(\phi)^2*(\cos(\theta)^2+\sin(\theta)^2)$$
$$+OP^2\cos(\phi))^2$$
$$\cos(\theta)^2+\sin(\theta)^2=1$$
그러므로
$$OP^2*\sin(\phi)^2*1+OP^2\cos(\phi))^2$$
가 됩니다.
정리하면
$$OP^2*\sin(\phi)^2+OP^2\cos(\phi)^2$$
다시한번
$$OP^2$$
으로 묶으면
$$OP^2*(\sin(\phi)^2+cos(\phi)^2)$$
됩니다.
그러면 마찬가지로 1이 되므로
$$OP^2*1$$입니다.
즉
$$x^2+y^2+z^2=OP^2$$
입니다.
그렇다면 각도의 값들은 어떻게 구할까요
위의 그림의 각도인
$$\theta , \phi$$
구해보겠습니다.
$$\phi=\arccos(z/OP)$$
$$\theta=\arctan(y/x)$$
인데 이를 증명해보이겠습니다.
먼저
$$z=OP*\cos(\phi)$$
이용하여 구해보겠습니다.
$$z/OP=cos(\phi)$$
$$\arccos(x)=cos (y)$$
$$\phi=acrccos(z/OP)$$
다음에는
$$\tan \theta=(y/x)$$
$$\arctan (x) =\tan (y)$$
$$\theta=\arctan (y/x)$$
이다